hot spot: a very hot part of the mantle, where magma can melt throught a plate moving above it.
vent: a central opening in the volcanic area throught wich magma may scape.
lava: magma that reaches Earth surface and flows out of a vent.
crater: a cuplike hollow that forms at the top of a volcano around the vent.
geothermal energy: heat from below Earth surface.
cinder cone volcano: a steep sided cone that forms from explosive eruptions of hot rocks, ranging from particles to boulders.
shield volcano: a wide, gently sloped cone that forms from flows of lava.
composite volcano: a cone formed from explosed eruption of hot rocks followed by a flow of lava, over and over.
In this blog i will put all the vocabularys i do in my science class. I hope you enjoy it.
domingo, 26 de septiembre de 2010
Vocabulary#13: Earthquakes
fault: a huge crack in the crust, at or below the surface, the sides of which may show evidence of motion.
focus: the point where an earthquake starts, where rocks begin to slide past each other.
seismic waves: a vibriation that spreads out away from a focus when am earthquake happens.
epicenter: the point on Earth surface directly above the focus.
aftershock: the shaking of the crust after the initial shaking of an earthquake.
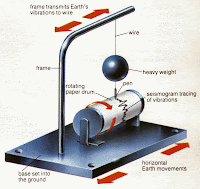
seismograph: a sensitive divice that detect the shaking of the crust.
magnitude: the amount of energy released by an earthquake.
focus: the point where an earthquake starts, where rocks begin to slide past each other.
seismic waves: a vibriation that spreads out away from a focus when am earthquake happens.
epicenter: the point on Earth surface directly above the focus.
aftershock: the shaking of the crust after the initial shaking of an earthquake.
seismograph: a sensitive divice that detect the shaking of the crust.
magnitude: the amount of energy released by an earthquake.
sábado, 25 de septiembre de 2010
Vocabulary#12:Moving Plates
Crust: Earth solid, rocky surface contaning the conteining the continents and ocean floor.
original horizontaly: the idea that some rocks or mountainsd where form by horizontal lines.
continental drift: the idea that in the past all the continents where together and that are still moving apart 1cm por year.
sea floor spriding: the idea that a new crust is forming under water sea floor.
magma: hot, molten rock below Earth surface.
plate tectonics: that earth is form by plates that moves.
mantle: Earth leyer beneath the crust.
subduction: where plates colide, the slidingof a denser oceanplate under another plate.
original horizontaly: the idea that some rocks or mountainsd where form by horizontal lines.
continental drift: the idea that in the past all the continents where together and that are still moving apart 1cm por year.
sea floor spriding: the idea that a new crust is forming under water sea floor.
magma: hot, molten rock below Earth surface.
plate tectonics: that earth is form by plates that moves.
mantle: Earth leyer beneath the crust.
subduction: where plates colide, the slidingof a denser oceanplate under another plate.
Vocabulary#11:Galaxys an Beyond
galaxy: a large group of stars held together by the gravity.
milky way: our home galaxy.
spectrum: a band of colors made when light white light is broken up.
expantion redshift: the shift of a spectrum of a galaxy toward longer (redder)wave lents to do the expansion of space.
big bang: the bigining of the univers, when the densyty of the universe was very haight.
background radietion: electromagnation radiotion left over the bing bang,
quasar: an extrimly bright, extrimly distant,hight energy source.
milky way: our home galaxy.
spectrum: a band of colors made when light white light is broken up.
expantion redshift: the shift of a spectrum of a galaxy toward longer (redder)wave lents to do the expansion of space.
big bang: the bigining of the univers, when the densyty of the universe was very haight.
background radietion: electromagnation radiotion left over the bing bang,
quasar: an extrimly bright, extrimly distant,hight energy source.
Vocabulary#10: Stars
star: a large, hot ball of gases, which is held together by gravity and gives off its own light.
Black hole: an object whoos gravity is so strong that light can not escape it.
parallax: the apparent shift in an object´s location when viewed from two positions.
Light year: the distance light trvels in a year.
constelletion: a number of stars that appear to form a pattern.
magnitude: the brightness of a star.
nebula: a cloud of gases and dust in space.
Black hole: an object whoos gravity is so strong that light can not escape it.
parallax: the apparent shift in an object´s location when viewed from two positions.
Light year: the distance light trvels in a year.
constelletion: a number of stars that appear to form a pattern.
magnitude: the brightness of a star.
nebula: a cloud of gases and dust in space.
super nova: a star that explodes.
Vocabulary#9 The Outer Solar System
Comet: a ball of rock and ice that orbit the sun.
Meteoroid: a small asteroid ( rocky object that orbit the sun ) , wich may be far out in the solar system or close to the inner planets.
meteor: a Meteoroid that enters Earth atmospher and borns with a strike of light.
meteorite: any part of the Meteoroid that reaches earth surface.
Meteoroid: a small asteroid ( rocky object that orbit the sun ) , wich may be far out in the solar system or close to the inner planets.
meteor: a Meteoroid that enters Earth atmospher and borns with a strike of light.
meteorite: any part of the Meteoroid that reaches earth surface.
Vocabulary#8: The Inner Solar System
planet: a large body orbiting a star , such as the Sun.
asteroid: a rocky, metalic object that orbit the sun.
solar system: a star such as the sun, and all objects orbiting it.
Kepler laws: laws that summarize the movment of the planets.
asteroid: a rocky, metalic object that orbit the sun.
solar system: a star such as the sun, and all objects orbiting it.
Kepler laws: laws that summarize the movment of the planets.
Vocabulary#7: The Moon in Motion
phase of the Moon: the shape of the lighted part of the Moon seen from Earthat any time.
lunar eclipse: a blocking of a view of the full moon when the moon passes into Earth shadow.
Solar eclipse: a bloking out of a view of the sun when the earth passe throught the moon shadow.
tide: the regular rise and fall of the water level along a shorline.
lunar eclipse: a blocking of a view of the full moon when the moon passes into Earth shadow.
Solar eclipse: a bloking out of a view of the sun when the earth passe throught the moon shadow.
tide: the regular rise and fall of the water level along a shorline.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)