This topic talk about wat we have learn in all this year in the blog.And a new topic name the type of blod that are A, B, AB, O. Also the cromosomes. Also talk about the Hemophelia is a great deseses. Our body have 23 chromosemes.
In this blog i will put all the vocabularys i do in my science class. I hope you enjoy it.
miércoles, 17 de noviembre de 2010
sábado, 13 de noviembre de 2010
How heredity Works
The different between mitosis and meiosis is that mitosis is the divition of the nucleus while a cell is dividing into 2 identical cells. And meiosis is the same but only ocure in the sex cell.
parts of a cell
What is the DNA? a DNA is a long, complex molecule that contains the codes that control your cells activiteas, your chemical makeup, and heredity.
Predicting traits
for predict traits we us a Punett Sqauare:
Example:
BB: full dominant
Bb: incomplete dominant
bb:rescecive
Trait: genes
Other think we use is the Pedigree:
Example:
Example:
BB: full dominant
Bb: incomplete dominant
bb:rescecive
Trait: genes
Other think we use is the Pedigree:
Example:
Learning About Heredity
What is a trait? A trait is a fisical characteristic pass to the parent to the offspring .Gregor Mendel is consider the father of the genetic he count the types of pea plants .
The types of polinations are self polination and cross polination
The types of polinations are self polination and cross polination
Geologic time
You some times hear scientis saing this two word relative age and absolute age and you dont now to wat they refer until today because i will explane you the diference of each one.
The diferent between relative age and absolute age is that relative age is the age that is no so much clear of some thing and absolute age is the age that is a 100% sure that that is the age.
There are 4 types of Eras Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Conozoic. And we live in the Era Cenozoic, Period Quaternary but I think that the chart below will help you to understand more.
The diferent between relative age and absolute age is that relative age is the age that is no so much clear of some thing and absolute age is the age that is a 100% sure that that is the age.
There are 4 types of Eras Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Conozoic. And we live in the Era Cenozoic, Period Quaternary but I think that the chart below will help you to understand more.
The Rock Cycle
In this topic we will learn about the rock cycle lets bigin:
first the volcano take out lava that roc is name Igneus rock then that rock go to the sand and transform into Sedimentary rock then it travel to the center of the earth whene it transform into Metamorphic rock and for last it transom into magma and the prosses continue and it never stops.
first the volcano take out lava that roc is name Igneus rock then that rock go to the sand and transform into Sedimentary rock then it travel to the center of the earth whene it transform into Metamorphic rock and for last it transom into magma and the prosses continue and it never stops.
Lift, Carry and Drop
Gravity affect materials by breaking down rocks in sedementary.that is call mass wasting . They are tree types of glaciars
- Valley Glaciar: Is form in the hight mountain valleys,where it is cold because of the elevation.
- Continental Glaciars: Is form near the poles,where it is cold because of the latitude.
- Narrower Glaciars: They dragged soil along. As they marged into one glacier, the soil became trapped in the middle, like a stream of soil.
miércoles, 27 de octubre de 2010
Building Up an Breaking Down
This topic talk about how mountains are form. Lets bigin with the types of mountains, there are two types the fold mountain and the fault block mountain. The fold mountain is a mountain maded of mostly of rock layers folded by being squeezed together.And the fault blog mountain is a mountain made by huge tilted blocks of rocks separated 0from soraunding rock by fault.
The different between weathering and erosion is that weathering is the breking down of pices of rocks and erosion is the proses that picking up of the rock pieces.The horizons are three name: Horizon A: has a lot of humus, Horizon B: have alittle amount of himes an Horizon C: is the bed rock
The different between weathering and erosion is that weathering is the breking down of pices of rocks and erosion is the proses that picking up of the rock pieces.The horizons are three name: Horizon A: has a lot of humus, Horizon B: have alittle amount of himes an Horizon C: is the bed rock
domingo, 26 de septiembre de 2010
Vocabulary#14: Volcanoes
hot spot: a very hot part of the mantle, where magma can melt throught a plate moving above it.
vent: a central opening in the volcanic area throught wich magma may scape.
lava: magma that reaches Earth surface and flows out of a vent.
crater: a cuplike hollow that forms at the top of a volcano around the vent.
geothermal energy: heat from below Earth surface.
cinder cone volcano: a steep sided cone that forms from explosive eruptions of hot rocks, ranging from particles to boulders.
shield volcano: a wide, gently sloped cone that forms from flows of lava.
composite volcano: a cone formed from explosed eruption of hot rocks followed by a flow of lava, over and over.
vent: a central opening in the volcanic area throught wich magma may scape.
lava: magma that reaches Earth surface and flows out of a vent.
crater: a cuplike hollow that forms at the top of a volcano around the vent.
geothermal energy: heat from below Earth surface.
cinder cone volcano: a steep sided cone that forms from explosive eruptions of hot rocks, ranging from particles to boulders.
shield volcano: a wide, gently sloped cone that forms from flows of lava.
composite volcano: a cone formed from explosed eruption of hot rocks followed by a flow of lava, over and over.
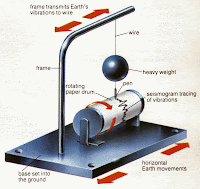
Vocabulary#13: Earthquakes
fault: a huge crack in the crust, at or below the surface, the sides of which may show evidence of motion.
focus: the point where an earthquake starts, where rocks begin to slide past each other.
seismic waves: a vibriation that spreads out away from a focus when am earthquake happens.
epicenter: the point on Earth surface directly above the focus.
aftershock: the shaking of the crust after the initial shaking of an earthquake.
seismograph: a sensitive divice that detect the shaking of the crust.
magnitude: the amount of energy released by an earthquake.
focus: the point where an earthquake starts, where rocks begin to slide past each other.
seismic waves: a vibriation that spreads out away from a focus when am earthquake happens.
epicenter: the point on Earth surface directly above the focus.
aftershock: the shaking of the crust after the initial shaking of an earthquake.
seismograph: a sensitive divice that detect the shaking of the crust.
magnitude: the amount of energy released by an earthquake.
sábado, 25 de septiembre de 2010
Vocabulary#12:Moving Plates
Crust: Earth solid, rocky surface contaning the conteining the continents and ocean floor.
original horizontaly: the idea that some rocks or mountainsd where form by horizontal lines.
continental drift: the idea that in the past all the continents where together and that are still moving apart 1cm por year.
sea floor spriding: the idea that a new crust is forming under water sea floor.
magma: hot, molten rock below Earth surface.
plate tectonics: that earth is form by plates that moves.
mantle: Earth leyer beneath the crust.
subduction: where plates colide, the slidingof a denser oceanplate under another plate.
original horizontaly: the idea that some rocks or mountainsd where form by horizontal lines.
continental drift: the idea that in the past all the continents where together and that are still moving apart 1cm por year.
sea floor spriding: the idea that a new crust is forming under water sea floor.
magma: hot, molten rock below Earth surface.
plate tectonics: that earth is form by plates that moves.
mantle: Earth leyer beneath the crust.
subduction: where plates colide, the slidingof a denser oceanplate under another plate.
Vocabulary#11:Galaxys an Beyond
galaxy: a large group of stars held together by the gravity.
milky way: our home galaxy.
spectrum: a band of colors made when light white light is broken up.
expantion redshift: the shift of a spectrum of a galaxy toward longer (redder)wave lents to do the expansion of space.
big bang: the bigining of the univers, when the densyty of the universe was very haight.
background radietion: electromagnation radiotion left over the bing bang,
quasar: an extrimly bright, extrimly distant,hight energy source.
milky way: our home galaxy.
spectrum: a band of colors made when light white light is broken up.
expantion redshift: the shift of a spectrum of a galaxy toward longer (redder)wave lents to do the expansion of space.
big bang: the bigining of the univers, when the densyty of the universe was very haight.
background radietion: electromagnation radiotion left over the bing bang,
quasar: an extrimly bright, extrimly distant,hight energy source.
Vocabulary#10: Stars
star: a large, hot ball of gases, which is held together by gravity and gives off its own light.
Black hole: an object whoos gravity is so strong that light can not escape it.
parallax: the apparent shift in an object´s location when viewed from two positions.
Light year: the distance light trvels in a year.
constelletion: a number of stars that appear to form a pattern.
magnitude: the brightness of a star.
nebula: a cloud of gases and dust in space.
Black hole: an object whoos gravity is so strong that light can not escape it.
parallax: the apparent shift in an object´s location when viewed from two positions.
Light year: the distance light trvels in a year.
constelletion: a number of stars that appear to form a pattern.
magnitude: the brightness of a star.
nebula: a cloud of gases and dust in space.
super nova: a star that explodes.
Vocabulary#9 The Outer Solar System
Comet: a ball of rock and ice that orbit the sun.
Meteoroid: a small asteroid ( rocky object that orbit the sun ) , wich may be far out in the solar system or close to the inner planets.
meteor: a Meteoroid that enters Earth atmospher and borns with a strike of light.
meteorite: any part of the Meteoroid that reaches earth surface.
Meteoroid: a small asteroid ( rocky object that orbit the sun ) , wich may be far out in the solar system or close to the inner planets.
meteor: a Meteoroid that enters Earth atmospher and borns with a strike of light.
meteorite: any part of the Meteoroid that reaches earth surface.
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)